linprog Solves a linear programming problem
Calling Sequence
xopt = linprog(c,A,b) xopt = linprog(c,A,b,Aeq,beq) xopt = linprog(c,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub) xopt = linprog(c,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,param) xopt = linprog(file) xopt = linprog(file,param) [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda] = linprog( ... )
Parameters
- c :
a vector of double, contains coefficients of the variables in the objective
- A :
a matrix of double, represents the linear coefficients in the inequality constraints A⋅x ≤ b.
- b :
a vector of double, represents the linear coefficients in the inequality constraints A⋅x ≤ b.
- Aeq :
a matrix of double, represents the linear coefficients in the equality constraints Aeq⋅x = beq.
- beq :
a vector of double, represents the linear coefficients in the equality constraints Aeq⋅x = beq.
- lb :
Lower bounds, specified as a vector or array of double. lb represents the lower bounds elementwise in lb ≤ x ≤ ub.
- ub :
Upper bounds, specified as a vector or array of double. ub represents the upper bounds elementwise in lb ≤ x ≤ ub.
- options :
a list containing the parameters to be set.
- file :
a string describing the path to the mps file.
- xopt :
a vector of double, the computed solution of the optimization problem.
- fopt :
a double, the value of the function at x.
- status :
status flag returned from symphony. See below for details.
- output :
The output data structure contains detailed information about the optimization process. See below for details.
- lambda :
The structure consist of the Lagrange multipliers at the solution of problem. See below for details.
Description
OSI-CLP is used for solving the linear programming problems, OSI-CLP is a library written in C++. Search the minimum of a constrained linear programming problem specified by :
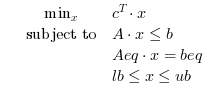
The routine calls Clp for solving the linear programming problem, Clp is a library written in C++.
The options allows the user to set various parameters of the Optimization problem. It should be defined as type "list" and contains the following fields. In the current version it only contains maxiter.
- Syntax : options= list("MaxIter", [---]);
- MaxIter : a Scalar, containing the Maximum Number of Iteration that the solver should take.
- Default Values : options = list("MaxIter", [3000]);
The exitflag allows to know the status of the optimization which is given back by CLP.
- exitflag=0 : Optimal Solution Found
- exitflag=1 : Primal Infeasible
- exitflag=2 : Dual Infeasible
- exitflag=3 : Maximum Number of Iterations Exceeded. Output may not be optimal.
- exitflag=4 : Solution Abandoned
- exitflag=5 : Primal objective limit reached.
- exitflag=6 : Dual objective limit reached.
The output data structure contains detailed informations about the optimization process. It has type "struct" and contains the following fields.
- output.iterations: The number of iterations performed during the search
- output.constrviolation: The max-norm of the constraint violation.
The lambda data structure contains the Lagrange multipliers at the end of optimization. In the current version the values are returned only when the the solution is optimal. It has type "struct" and contains the following fields.
- lambda.lower: The Lagrange multipliers for variable lower bounds.
- lambda.eqlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the linear equality constraints.
- lambda.ineqlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the linear inequality constraints.
Examples
//Optimal problems //Linear program, linear inequality constraints c=[-1,-1/3]' A=[1,1;1,1/4;1,-1;-1/4,-1;-1,-1;-1,1] b=[2,1,2,1,-1,2] [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]=linprog(c, A, b) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//Linear program with Linear Inequalities and Equalities` c=[-1,-1/3]' A=[1,1;1,1/4;1,-1;-1/4,-1;-1,-1;-1,1] b=[2,1,2,1,-1,2] Aeq=[1,1/4] beq=[1/2] [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]=linprog(c, A, b, Aeq, beq) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//Linear program with all constraint types c=[-1,-1/3]' A=[1,1;1,1/4;1,-1;-1/4,-1;-1,-1;-1,1] b=[2,1,2,1,-1,2] Aeq=[1,1/4] beq=[1/2] lb=[-1,-0.5] ub=[1.5,1.25] [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]=linprog(c, A, b, Aeq, beq, lb, ub) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//Primal Infeasible Problem c=[-1,-1,-1]' A=[1,2,-1] b=[-4] Aeq=[1,5,3;1,1,0] beq=[10,100] lb=[0,0,0] ub=[%inf,%inf,%inf] [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]= linprog(c,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//Dual Infeasible Problem c=[3,5,-7]' A=[-1,-1,4;1,1,4] b=[-8,5] Aeq=[] beq=[] lb=[-%inf,-%inf,-%inf] ub=[%inf,%inf,%inf] [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]= linprog(c,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
filepath = get_absolute_file_path('linprog.dem.sce'); filepath = filepath + "exmip1.mps" [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda] =linprog(filepath) |
Authors
- Bhanu Priya Sayal, Guru Pradeep Reddy