fmincon Solves a multi-variable constrainted optimization problem
Calling Sequence
xopt = fmincon(f,x0,A,b) xopt = fmincon(f,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq) xopt = fmincon(f,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub) xopt = fmincon(f,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nlc) xopt = fmincon(f,x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nlc,options) [xopt,fopt] = fmincon(.....) [xopt,fopt,exitflag]= fmincon(.....) [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output]= fmincon(.....) [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda]=fmincon(.....) [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda,gradient]=fmincon(.....) [xopt,fopt,exitflag,output,lambda,gradient,hessian]=fmincon(.....)
Parameters
- f :
a function, representing the objective function of the problem
- x0 :
a vector of doubles, containing the starting values of variables of size (1 X n) or (n X 1) where 'n' is the number of Variables
- A :
a matrix of doubles, containing the coefficients of linear inequality constraints of size (m X n) where 'm' is the number of linear inequality constraints
- b :
a vector of doubles, related to 'A' and containing the the Right hand side equation of the linear inequality constraints of size (m X 1)
- Aeq :
a matrix of doubles, containing the coefficients of linear equality constraints of size (m1 X n) where 'm1' is the number of linear equality constraints
- beq :
a vector of doubles, related to 'Aeq' and containing the the Right hand side equation of the linear equality constraints of size (m1 X 1)
- lb :
a vector of doubles, containing the lower bounds of the variables of size (1 X n) or (n X 1) where 'n' is the number of Variables
- ub :
a vector of doubles, containing the upper bounds of the variables of size (1 X n) or (n X 1) where 'n' is the number of Variables
- nlc :
a function, representing the Non-linear Constraints functions(both Equality and Inequality) of the problem. It is declared in such a way that non-linear inequality constraints are defined first as a single row vector (c), followed by non-linear equality constraints as another single row vector (ceq). Refer Example for definition of Constraint function.
- options :
a list, containing the option for user to specify. See below for details.
- xopt :
a vector of doubles, cointating the computed solution of the optimization problem
- fopt :
a scalar of double, containing the the function value at x
- exitflag :
a scalar of integer, containing the flag which denotes the reason for termination of algorithm. See below for details.
- output :
a structure, containing the information about the optimization. See below for details.
- lambda :
a structure, containing the Lagrange multipliers of lower bound, upper bound and constraints at the optimized point. See below for details.
- gradient :
a vector of doubles, containing the Objective's gradient of the solution.
- hessian :
a matrix of doubles, containing the Lagrangian's hessian of the solution.
Description
Search the minimum of a constrained optimization problem specified by : Find the minimum of f(x) such that
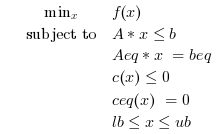
The routine calls Ipopt for solving the Constrained Optimization problem, Ipopt is a library written in C++.
The options allows the user to set various parameters of the Optimization problem. It should be defined as type "list" and contains the following fields.
- Syntax : options= list("MaxIter", [---], "CpuTime", [---], "GradObj", ---, "Hessian", ---, "GradCon", ---);
- MaxIter : a Scalar, containing the Maximum Number of Iteration that the solver should take.
- CpuTime : a Scalar, containing the Maximum amount of CPU Time that the solver should take.
- GradObj : a function, representing the gradient function of the Objective in Vector Form.
- Hessian : a function, representing the hessian function of the Lagrange in Symmetric Matrix Form with Input parameters x, Objective factor and Lambda. Refer Example for definition of Lagrangian Hessian function.
- GradCon : a function, representing the gradient of the Non-Linear Constraints (both Equality and Inequality) of the problem. It is declared in such a way that gradient of non-linear inequality constraints are defined first as a separate Matrix (cg of size m2 X n or as an empty), followed by gradient of non-linear equality constraints as a separate Matrix (ceqg of size m2 X n or as an empty) where m2 & m3 are number of non-linear inequality and equality constraints respectively.
- Default Values : options = list("MaxIter", [3000], "CpuTime", [600]);
The exitflag allows to know the status of the optimization which is given back by Ipopt.
- exitflag=0 : Optimal Solution Found
- exitflag=1 : Maximum Number of Iterations Exceeded. Output may not be optimal.
- exitflag=2 : Maximum amount of CPU Time exceeded. Output may not be optimal.
- exitflag=3 : Stop at Tiny Step.
- exitflag=4 : Solved To Acceptable Level.
- exitflag=5 : Converged to a point of local infeasibility.
For more details on exitflag see the ipopt documentation, go to http://www.coin-or.org/Ipopt/documentation/
The output data structure contains detailed informations about the optimization process. It has type "struct" and contains the following fields.
- output.Iterations: The number of iterations performed during the search
- output.Cpu_Time: The total cpu-time spend during the search
- output.Objective_Evaluation: The number of Objective Evaluations performed during the search
- output.Dual_Infeasibility: The Dual Infeasiblity of the final soution
The lambda data structure contains the Lagrange multipliers at the end of optimization. In the current version the values are returned only when the the solution is optimal. It has type "struct" and contains the following fields.
- lambda.lower: The Lagrange multipliers for the lower bound constraints.
- lambda.upper: The Lagrange multipliers for the upper bound constraints.
- lambda.eqlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the linear equality constraints.
- lambda.ineqlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the linear inequality constraints.
- lambda.eqnonlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the non-linear equality constraints.
- lambda.ineqnonlin: The Lagrange multipliers for the non-linear inequality constraints.
Examples
//Find x in R^2 such that it minimizes: //f(x)= -x1 -x2/3 //x0=[0,0] //constraint-1 (c1): x1 + x2 <= 2 //constraint-2 (c2): x1 + x2/4 <= 1 //constraint-3 (c3): x1 - x2 <= 2 //constraint-4 (c4): -x1/4 - x2 <= 1 //constraint-5 (c5): -x1 - x2 <= -1 //constraint-6 (c6): -x1 + x2 <= 2 //constraint-7 (c7): x1 + x2 = 2 //Objective function to be minimised function y=f(x) y=-x(1)-x(2)/3; endfunction //Starting point, linear constraints and variable bounds x0=[0 , 0]; A=[1,1 ; 1,1/4 ; 1,-1 ; -1/4,-1 ; -1,-1 ; -1,1]; b=[2;1;2;1;-1;2]; Aeq=[1,1]; beq=[2]; lb=[]; ub=[]; nlc=[]; //Gradient of objective function function y=fGrad(x) y= [-1,-1/3]; endfunction //Hessian of lagrangian function y=lHess(x, obj, lambda) y= obj*[0,0;0,0] endfunction //Options options=list("GradObj", fGrad, "Hessian", lHess); //Calling Ipopt [x,fval,exitflag,output,lambda,grad,hessian] =fmincon(f, x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nlc,options) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//Find x in R^3 such that it minimizes: //f(x)= x1*x2 + x2*x3 //x0=[0.1 , 0.1 , 0.1] //constraint-1 (c1): x1^2 - x2^2 + x3^2 <= 2 //constraint-2 (c2): x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2 <= 10 //Objective function to be minimised function y=f(x) y=x(1)*x(2)+x(2)*x(3); endfunction //Starting point, linear constraints and variable bounds x0=[0.1 , 0.1 , 0.1]; A=[]; b=[]; Aeq=[]; beq=[]; lb=[]; ub=[]; //Nonlinear constraints function [c, ceq]=nlc(x) c = [x(1)^2 - x(2)^2 + x(3)^2 - 2 , x(1)^2 + x(2)^2 + x(3)^2 - 10]; ceq = []; endfunction //Gradient of objective function function y=fGrad(x) y= [x(2),x(1)+x(3),x(2)]; endfunction //Hessian of the Lagrange Function function y=lHess(x, obj, lambda) y= obj*[0,1,0;1,0,1;0,1,0] + lambda(1)*[2,0,0;0,-2,0;0,0,2] + lambda(2)*[2,0,0;0,2,0;0,0,2] endfunction //Gradient of Non-Linear Constraints function [cg, ceqg]=cGrad(x) cg=[2*x(1) , -2*x(2) , 2*x(3) ; 2*x(1) , 2*x(2) , 2*x(3)]; ceqg=[]; endfunction //Options options=list("MaxIter", [1500], "CpuTime", [500], "GradObj", fGrad, "Hessian", lHess,"GradCon", cGrad); //Calling Ipopt [x,fval,exitflag,output] =fmincon(f, x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nlc,options) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//The below problem is an unbounded problem: //Find x in R^3 such that it minimizes: //f(x)= -(x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2) //x0=[0.1 , 0.1 , 0.1] // x1 <= 0 // x2 <= 0 // x3 <= 0 //Objective function to be minimised function y=f(x) y=-(x(1)^2+x(2)^2+x(3)^2); endfunction //Starting point, linear constraints and variable bounds x0=[0.1 , 0.1 , 0.1]; A=[]; b=[]; Aeq=[]; beq=[]; lb=[]; ub=[0,0,0]; //Options options=list("MaxIter", [1500], "CpuTime", [500]); //Calling Ipopt [x,fval,exitflag,output,lambda,grad,hessian] =fmincon(f, x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,[],options) // Press ENTER to continue |
Examples
//The below problem is an infeasible problem: //Find x in R^3 such that in minimizes: //f(x)=x1*x2 + x2*x3 //x0=[1,1,1] //constraint-1 (c1): x1^2 <= 1 //constraint-2 (c2): x1^2 + x2^2 <= 1 //constraint-3 (c3): x3^2 <= 1 //constraint-4 (c4): x1^3 = 0.5 //constraint-5 (c5): x2^2 + x3^2 = 0.75 // 0 <= x1 <=0.6 // 0.2 <= x2 <= inf // -inf <= x3 <= 1 //Objective function to be minimised function y=f(x) y=x(1)*x(2)+x(2)*x(3); endfunction //Starting point, linear constraints and variable bounds x0=[1,1,1]; A=[]; b=[]; Aeq=[]; beq=[]; lb=[0 0.2,-%inf]; ub=[0.6 %inf,1]; //Nonlinear constraints function [c, ceq]=nlc(x) c=[x(1)^2-1,x(1)^2+x(2)^2-1,x(3)^2-1]; ceq=[x(1)^3-0.5,x(2)^2+x(3)^2-0.75]; endfunction //Gradient of objective function function y=fGrad(x) y= [x(2),x(1)+x(3),x(2)]; endfunction //Hessian of the Lagrange Function function y=lHess(x, obj, lambda) y= obj*[0,1,0;1,0,1;0,1,0] + lambda(1)*[2,0,0;0,0,0;0,0,0] + lambda(2)*[2,0,0;0,2,0;0,0,0] +lambda(3)*[0,0,0;0,0,0;0,0,2] + lambda(4)*[6*x(1 ),0,0;0,0,0;0,0,0] + lambda(5)*[0,0,0;0,2,0;0,0,2]; endfunction //Gradient of Non-Linear Constraints function [cg, ceqg]=cGrad(x) cg = [2*x(1),0,0;2*x(1),2*x(2),0;0,0,2*x(3)]; ceqg = [3*x(1)^2,0,0;0,2*x(2),2*x(3)]; endfunction //Options options=list("MaxIter", [1500], "CpuTime", [500], "GradObj", fGrad, "Hessian", lHess,"GradCon", cGrad); //Calling Ipopt [x,fval,exitflag,output,lambda,grad,hessian] =fmincon(f, x0,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,nlc,options) |
Authors
- R.Vidyadhar , Vignesh Kannan